|
|
Global - Socket Pools
Socket pools are designed to allow Fortitude HTTP to share a common port between multiple websites. They can also be
used to pool resources for a subset of websites and bind to specific IP addresses (or all IP addresses) and to balance
throughput capabilities and memory load. Every website requires a socket pool, without one - the website cannot be started.
Socket Pools
Allows the server administrator to add, edit, delete and reorder server socket pools.
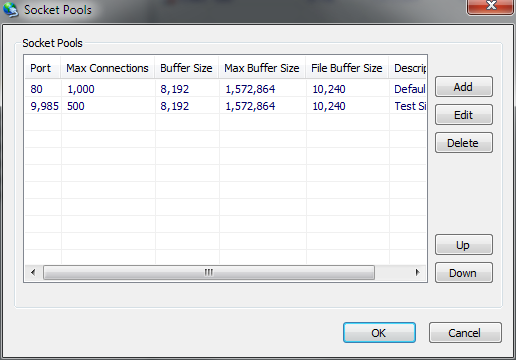
Socket Pools - Item - Basic
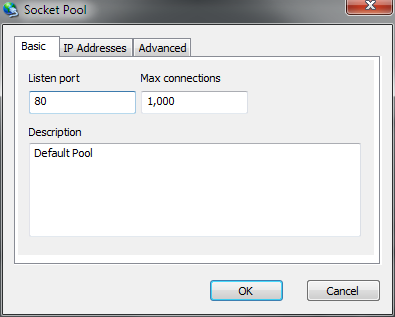
| Listen Port |
Specifies the TCP/IP port which the socket pool should bind and listen on. |
| Max Connections |
Specifies the maximum number of connections which the pool will allow to connect before enforcing disconnection of new peers. |
Socket Pools - Item - IP Addresses
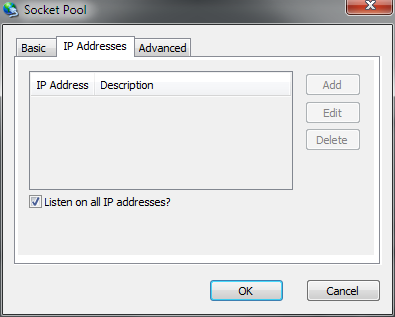
| IP Address |
Allows the server to listen on the configured pools port on a specific IP address. |
| Listen on all IP Addresses |
Causes the socket pool to listen on the configured port on all available IP addresses. |
Socket Pools - Item - Advanced
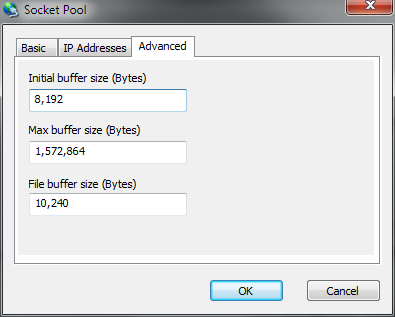
| Initial Buffer Size |
Sets the initial size of each connected peers send and receive buffers. If the remote
peer cannot receive data fast enough, then the buffer will be resized up to the Max
Buffer Size. The same applies to receiving; when the server can't process received
data quickly enough, the buffer resized to store received data up to the Max Buffer Size.
|
| Max Buffer Size |
Defines the maximum size of the internal per-connection data-pump buffer size. The buffer size is automatically resized as needed, typically due to an inability of the file system or network layers to keep-up with demand. This setting can be used to limit the amount of memory which will be consumed for this purpose. Can be set to 0 to allow the buffer to grow restriction. See [Initial Buffer Size] for more information. |
| File Buffer Size |
The file buffer size defines the number of bytes at a time which will be read at a time when handing file I/O operations (such as compression and reading from the disk for network transmission to a connected peer). Higher setting generally increase throughput but will demand more memory. See [Initial Buffer Size] for more information. |
|
|
|





